
What is SSL
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer. It is an internet protocol for securing data transfer between a user’s browser and the website they are visiting.
Every internet user transfers information when they visit websites. This information can often be sensitive like payment details, credit card information, or login credentials.
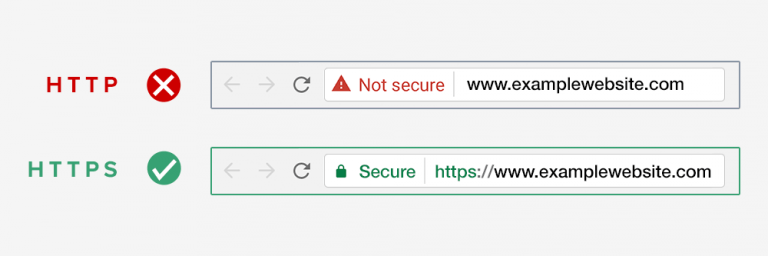
Using the normal HTTP protocol means this information can be hijacked by hackers. This is where SSL or HTTPS comes in.
Websites need an SSL certificate issued by one of the recognized certificate issuing authority. This certificate is verified and highlighted in the user’s browser address bar with a padlock sign and HTTPS instead of HTTP.
What information does an SSL certificate contain?
SSL certificates include:
- The domain name that the certificate was issued for
- Which person, organization, or device it was issued to
- Which certificate authority issued it
- The certificate authority’s digital signature
- Associated subdomains
- Issue date of the certificate
- Expiration date of the certificate
- The public key (the private key is kept secret)
The public and private keys used for SSL are essentially long strings of characters used for encrypting and decrypting data. Data encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key, and vice versa.
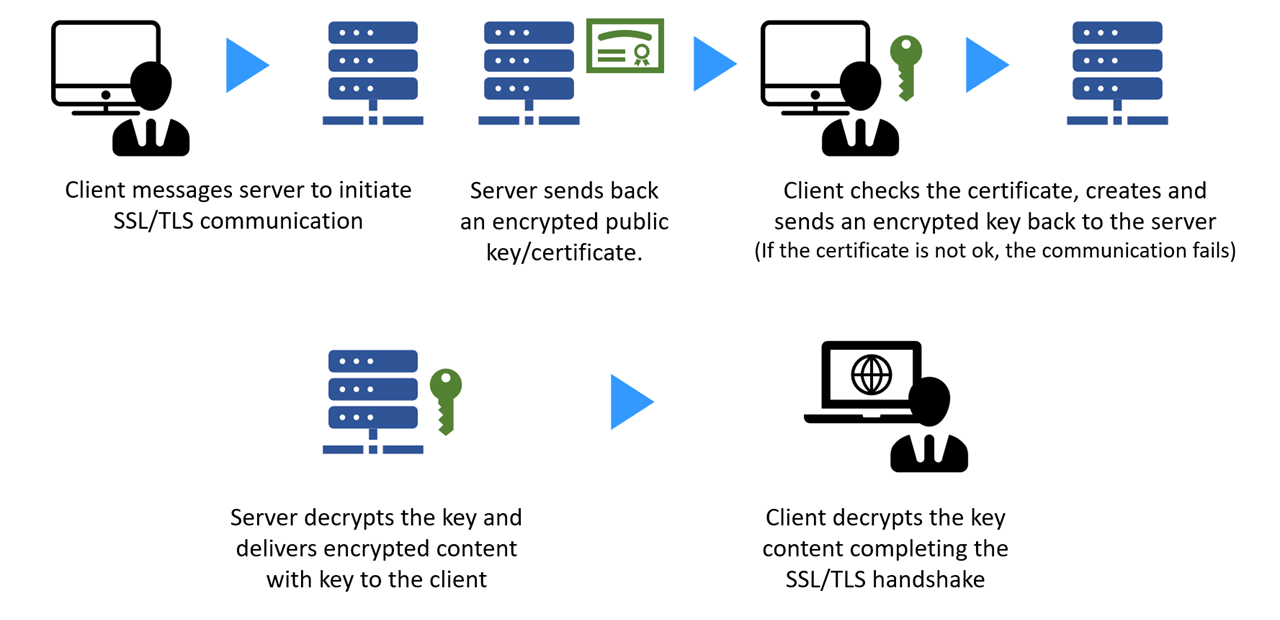
How does SSL Certificate work?
SSL Certificate providers we partner with





