What is the Internet of Things?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the billions of physical devices around the world that are now connected to the internet, all collecting and sharing data. Thanks to the arrival of super-cheap computer chips and the ubiquity of wireless networks, it’s possible to turn anything, from something as small as a pill to something as big as an aeroplane, into a part of the IoT. Connecting up all these different objects and adding sensors to them adds a level of digital intelligence to devices that would be otherwise dumb, enabling them to communicate real-time data without involving a human being. The Internet of Things is making the fabric of the world around us more smarter and more responsive, merging the digital and physical universes.
Top 10 IoT Sensor Types
- Temperature Sensor
- Humidity Sensor
- Pressure Sensor
- Proximity Sensor
- Level Sensor
- Accelerometers
- Gyroscope Sensor
- Gas Sensor
- Infrared Sensor
- Optical Sensor
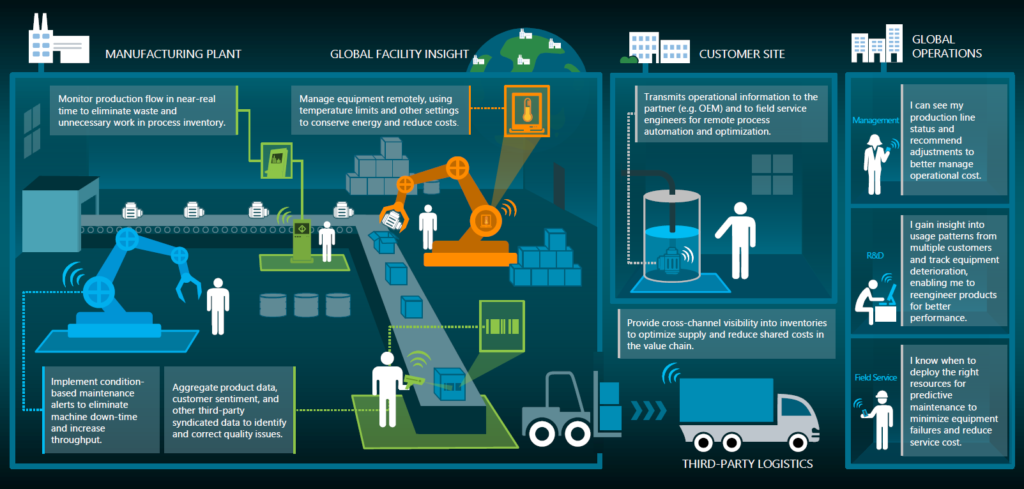
IoT in manufacturing
- Monitor production flow in near-real-time to eliminate waste and unnecessary work in process inventory.
- Manage equipment remotely, using temperature limits and other settings to conserve energy and reduce costs.
- Implement condition-based maintenance alerts to eliminate machine downtime and increase throughput.
- Aggregate product data, customer sentiment, and other third-party syndicated data to identify and correct quality issues.
- Transmit operational information to the partner(e.g. OEM) and to field service engineers for remote process automation and optimization.
- Provide cross-channel visibility into inventories to optimize supply and reduce shared costs in the value chain.
- See production line status and recommend adjustments to better manage operational costs.
- Gain insight into usage patterns from multiple customers and track equipment deterioration, enabling to reengineer products for better performance.
- Know when to deploy the right resources for predictive maintenance to minimize equipment failures and reduce service costs.